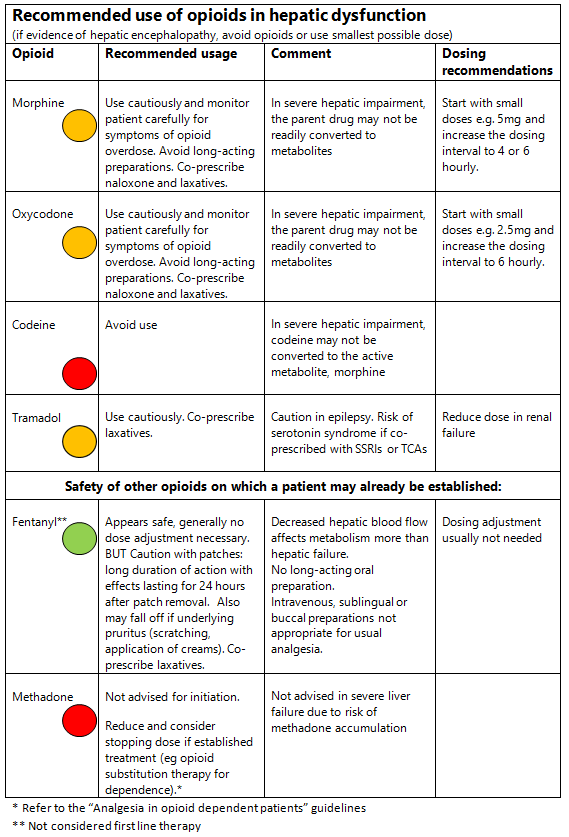
Analgesia in Hepatic Impairment
Non-Opioid Analgesics
Paracetamol : reduce dose to 1g tds [ref 4]
NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors: avoid in cirrhosis
Antidepressants: start at low dose as patients will be more susceptible to sedation and anti-cholinergic effects. Nortriptyline preferred over Amitriptyline . [ref 4] Duloxetine is not recommended in hepatic failure.
Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin and Pregabalin are not hepatically metabolized so are safer but patients will be more susceptible to sedation, nausea and dizziness. Avoid carbamazepine.
Recommended initial analgesic prescribing for moderate to severe hepatic failure

If neuropathic pain, consider regular Gabapentin 100mg tds (regular) as an initial dose.
Ensure regular pain assessment ( Basic Principles). Morphine doses can be cautiously increased as tolerated if pain is not well controlled. Consider stopping tramadol and prescribing regular sevredol QDS, in addition to PRN sevredol, if constant, background pain, is poorly controlled. The regular sevredol will be easier to titrate than modified-release morphine (eg MST) which should be avoided.